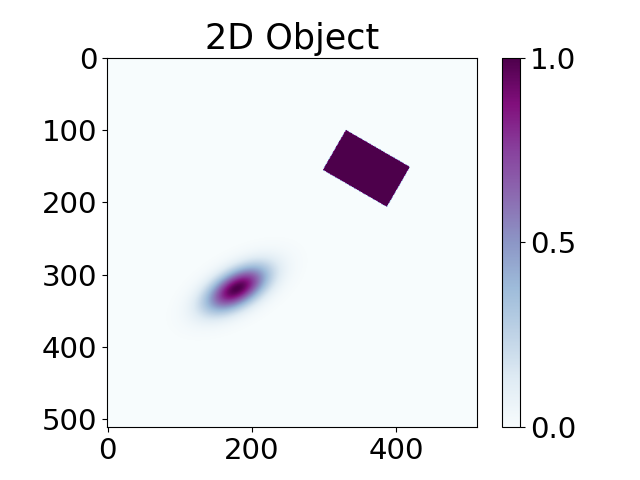
Phantoms using objects#
This tutorial shows how to build 2D phantom using Object and without Library files. One can also see Demos on how to build 3D or dynamic phantoms and hands-on experience.
from tomophantom import TomoP2D
from tomophantom.TomoP2D import Objects2D
N_size = 512 # define the size of the phantom
# define objects and parameters:
pp = {
"Obj": Objects2D.GAUSSIAN,
"C0": 1.00,
"x0": 0.25,
"y0": -0.3,
"a": 0.15,
"b": 0.3,
"phi": -30.0,
}
pp1 = {
"Obj": Objects2D.RECTANGLE,
"C0": 1.00,
"x0": -0.2,
"y0": 0.2,
"a": 0.25,
"b": 0.4,
"phi": 60.0,
}
myObjects = [pp, pp1] # dictionary of objects
phantom = TomoP2D.Object(N_size, myObjects)
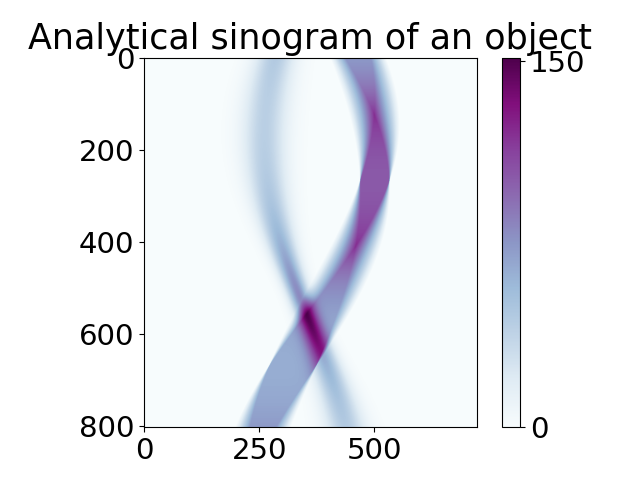
Using the list of dictionaries myObjects created above, we can now generate a sinogram for that phantom.
angles_num = int(0.5 * np.pi * N_size)
angles = np.linspace(0, 180, angles_num, dtype="float32")
angles_rad = angles * (np.pi / 180)
P = int(np.sqrt(2) * N_size) # detectors size
sino_an = TomoP2D.ObjectSino(N_size, P, angles, myObjects)