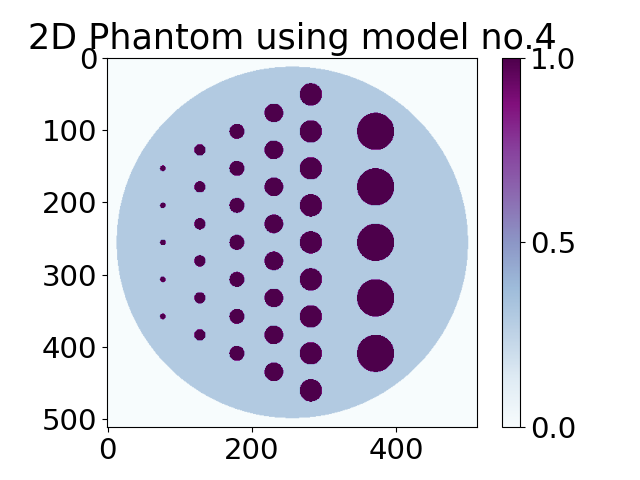
Phantoms using models#
This tutorial shows how to build 2D phantoms using already pre-existing Model stored in Library files. One can also see Demos on how to build 3D or dynamic phantoms and hands-on experience.
import tomophantom
from tomophantom import TomoP2D
model = 4 # select a model number from the library file (Phantom2DLibrary)
N_size = 512 # set the desired dimension of the phantom
path = os.path.dirname(tomophantom.__file__)
path_library2D = os.path.join(path, "phantomlib", "Phantom2DLibrary.dat") # path to the parameters file
phantom_2D = TomoP2D.Model(model, N_size, path_library2D) # Generate a N_size x N_size phantom (2D)
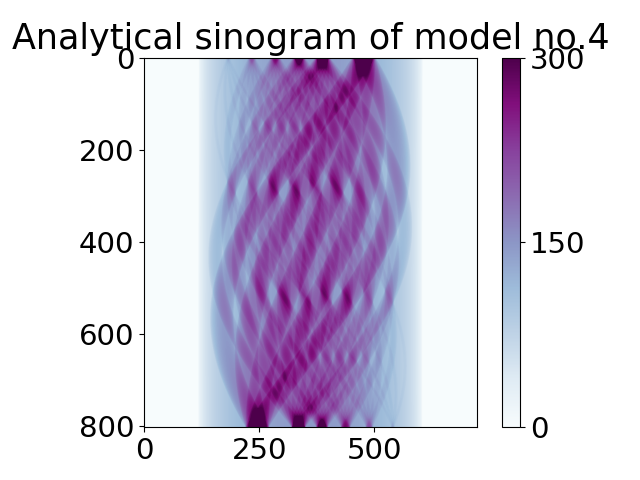
One can also create a projection data (sinogram for 2D phantom) by pointing to the same model number in the library file.
import tomophantom
from tomophantom import TomoP2D
model = 4 # select a model number from the library file (Phantom2DLibrary)
N_size = 512 # set the desired dimension of the phantom
path = os.path.dirname(tomophantom.__file__)
path_library2D = os.path.join(path, "phantomlib", "Phantom2DLibrary.dat") # path to the parameters file
# Parameters to generate a sinogram
angles_num = int(0.5 * np.pi * N_size)
angles = np.linspace(0.0, 179.9, angles_num, dtype="float32")
P = int(np.sqrt(2) * N_size) # detectors size
# create sinogram analytically
sino_an = TomoP2D.ModelSino(model, N_size, P, angles, path_library2D)