About TomoPhantom#
The general concept#
The variety of image processing techniques, such as, reconstruction, denoising, deblurring, inpainting, and segmentation require simulated ground truth data in order to numerically verify, benchmark and evaluate the proposed methods. The ground truth data can have various characteristics specific to the acquisition hardware, which also can be the focus of image processing method developers. In many situations, however, over-simplistic or unsuitable simulated data are used for testing.
In TomoPhantom, projection data is calculated following analytical Radon transform derivations applied to elementary functions. This approach is different to conventional numerical calculation of projections for the forward X-ray acquisition model using ray-tracing algorithms. Analytical projections are exact and discretized over a different grid which normally used for projection and backprojection steps in reconstruction methods. TomoPhantom enables a convenient testing environment for novel reconstruction methods, therefore avoiding the “inverse crime” issue (data simulation using the same grid). Overall, the use of exact projections and known ground truth is especially beneficial for benchmarking of iterative reconstruction algorithms.
TomoPhantom also offers simple linear dynamic extensions of 2D and 3D phantoms.
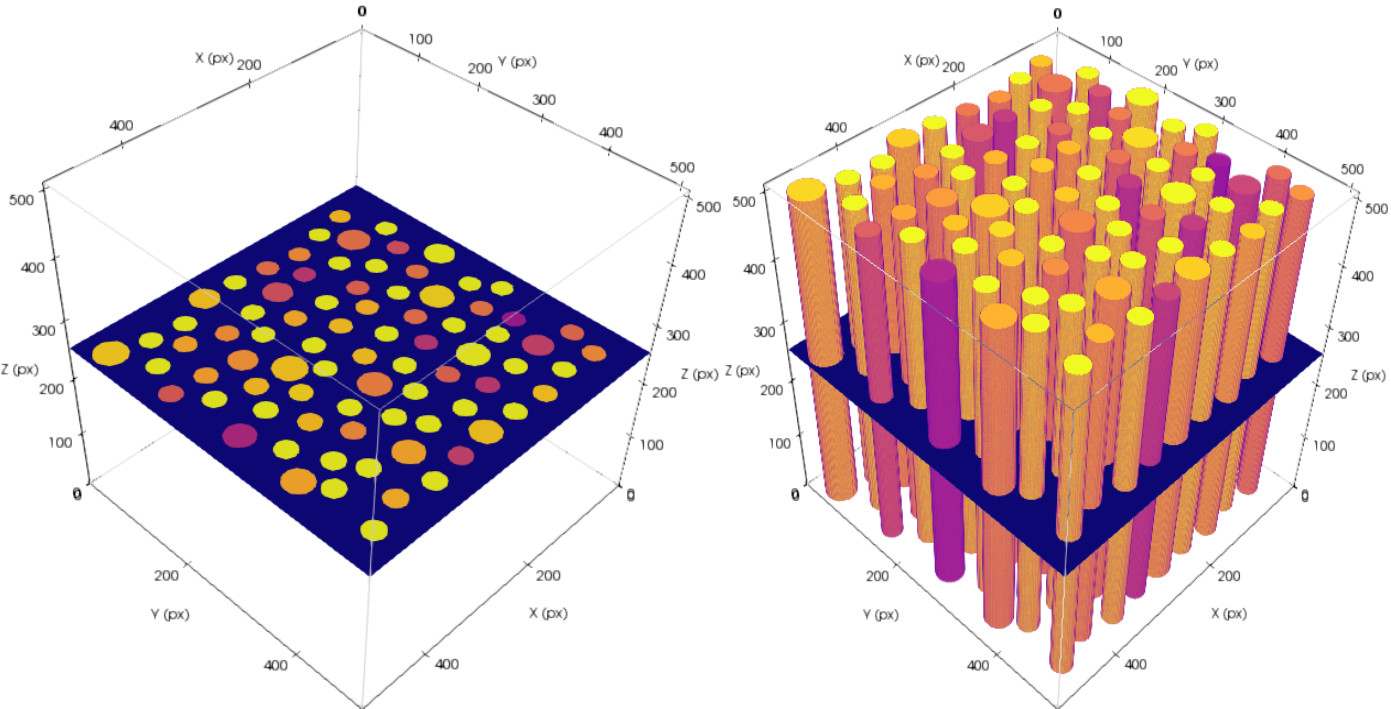
The generated TomoPhantom projection data is compatible with widely-used open-source tomographic reconstruction software, such as, ASTRA-toolbox and TomoPy packages.
What TomoPhantom can do#
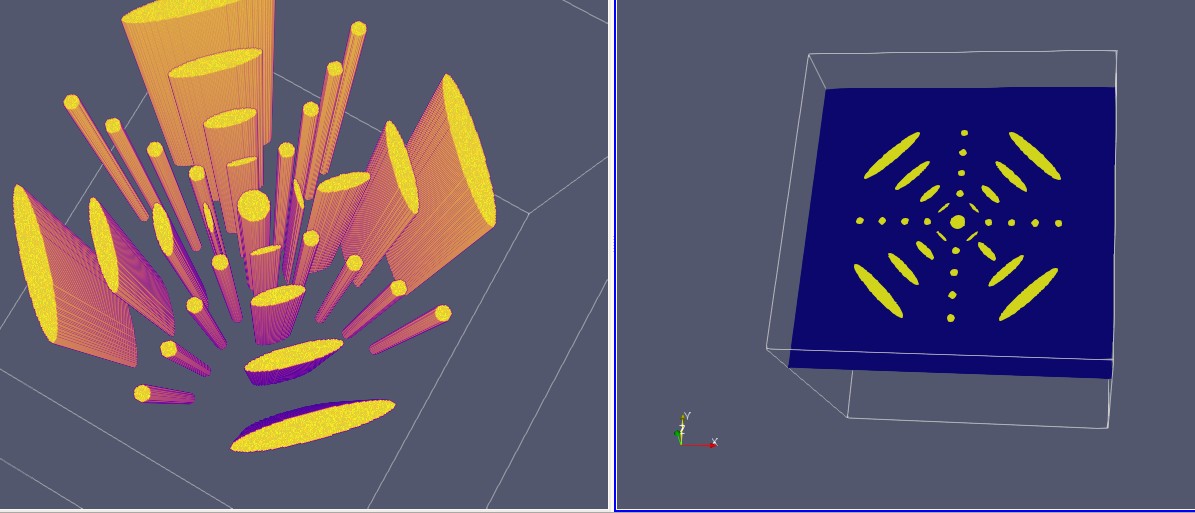
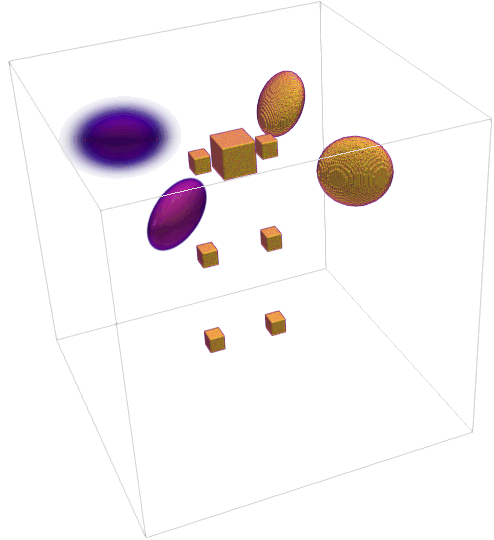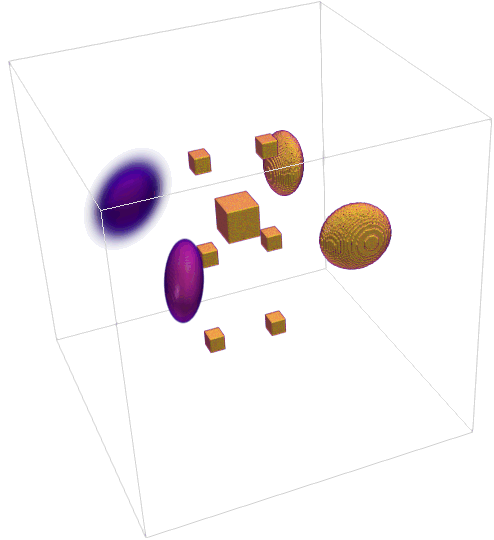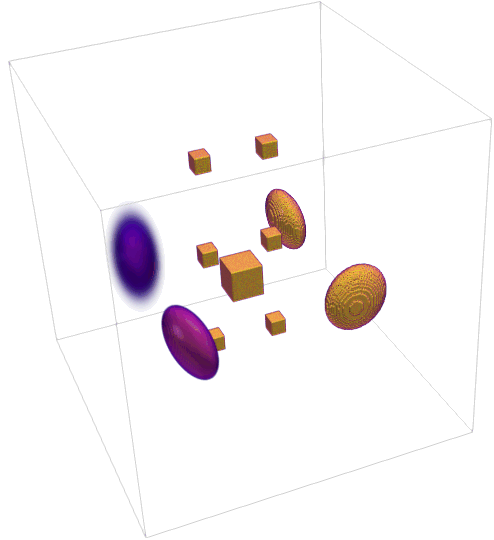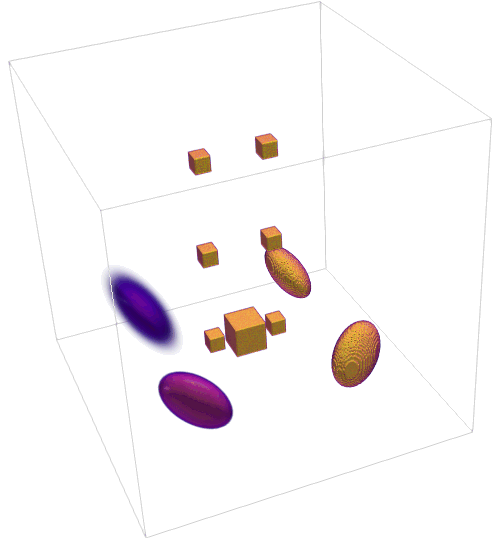
Generate 2D and 3D synthetic phantoms made of Gaussians, parabolas, ellipses, cones and rectangulars.
Generate simple temporal extensions of 2D and 3D phantoms.
Calculate analytical Radon transforms of 2D-4D models and also their numerical projections.
Model a variety of tomographic data artefacts (noise models, zingers, rings, shifts, partial volume effect and others).